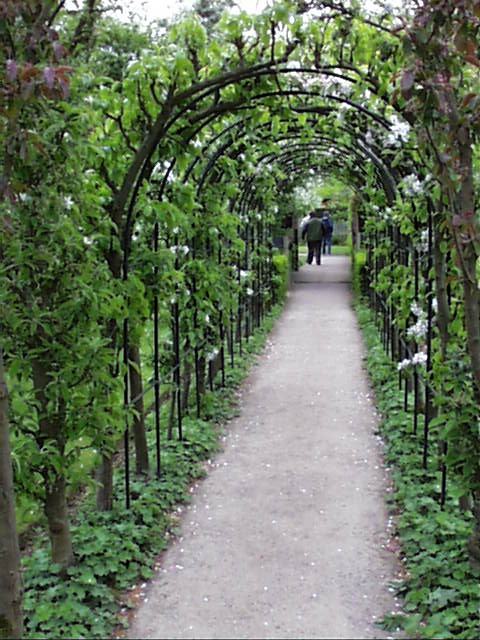
Roses are one of the splendours of the gardens
The Peckovers – a quaker banking family – left behind them a secret gem of a house and garden in Wisbech, Cambridgeshire. This is one ‘banker’s bonus’ that can be shared by everyone.
Peckover House is said to be one of the finest Georgian town houses in the country. It stands proudly fronting the River Nene in this Fenland market town of 20,000 people. Originally built in 1722, the house was initially rented by the Peckovers in 1794, and purchased soon after. Jonathan Peckover had a grocery business and then moved into banking, setting up the first bank in Wisbech in partnership with the Gurney family- who later founded Barclays Bank. Peckover established a good reputation – it was said that during times of financial crisis the Peckover Bank was safer than the Bank of England!
Peckover House was initially called Bank House, reflecting the role of the house and it’s newly built banking wing. The property remained in the family for over 150 years, eventually passing over to the National Trust from its last owner, Alexandrina Peckover, in 1948.
The gardens – of around 2 acres – extend to the rear of the house and grew over the years as the family purchased ground from adjacent landowners. They also included a much larger estate extending to 48 acres, much of which today is used as playing fields and has some character-ful old trees. The Peckovers were also keen collectors, and introduced a number of foreign plants into the garden. The gardens today maintain the basic layout from Victorian times – including the old walls that used to mark the boundaries of adjacent properties.

The rear of the house with the Croquet lawn in front- surrounded by some glorious trees such as the Tulip Tree (Liriodendron tulipifera)
Step out into the garden and you feel as though you are back in Victorian times, as you move from one delightful space to another.
Once needing a team of 17 gardeners, todays gardening team of three is headed up by Allison Napier. She finds it difficult to single out her favourite part of the garden – ‘It depends on the time of year’, she says. ‘In late winter and early spring the Wilderness Walk is full of the colours and scents from bulbs, Hellebores, Winter Honeysuckle, Christmas Box and an impressive Cornus mas. There is also the fantastic trunk of an old Ginkgo which stands out and this with surrounding evergreens, deciduous shrubs and trees creates a strong framework.’
‘In spring the Orangery is a riot of colour and fragrance from the various bulbs and other spring plants all arranged in terracotta pots on the staging and if the flowering of the Wisteria on the front of the house coincides with the wall flowers in the various formal beds at their peak, then that is a wonderful spot.’

Inside the Orangery- a heady mix of seasonal colour and fragrance
And what about the summer? The various rose gardens come into their own. There are over 60 species of rose here, many lovingly pruned and tied in every year over several metal pergolas and against walls. The area christened ‘Alexandrina’s Rose Garden‘ is a particular focal point.
But the show isn’t over yet. In late summer and autumn a ‘Red Border’ provides an array of warm colours and varied textures which are set off brilliantly against a golden privet hedge. This and an Autumn Border provide a glorious conclusion to the year. Jenny Windsor, one of the gardening team, loves these herbaceous borders and especially the contrast that they offer to other, more formal areas of the garden. ‘I love nothing more than to ‘have a play’ in the borders,’ she says – ‘weeding, dead heading, tying in etc.’

Herbaceous borders surrounding the Orchard Lawn with a fine old Quince tree
Many first-time visitors are surprised at the size and variety of plants in the garden. And, not surprisingly, they also commend the high standards of care maintained by the team.
Very few chemicals are used in the gardens and Allison finds that biological controls are effective in the glasshouses. As she says,
‘The healthy populations of beneficial insects, frogs and birds in the garden are testament to the ‘greener gardening’ policies we like to follow.’

The orangery (left) has rotten timbers and is due for a major renovation this year
The gardening team is well supported by local volunteers and a small number of trainees who come to gain practical horticultural experience (as I know, because I had the pleasure of being one last year!). Allison also thinks it important to encourage future generations of potential gardeners, so the team actively seeks school visits and has a Garden Club with students from the local grammar school.

Gardeners Jenny and Janet digging over and mulching the ‘Red Border’
What of the future? Well,the forthcoming restoration of the Orangery – with its 300 year old orange trees – is a major project due to get under way this year. Allison plans to complete work on the Conservation Plan for the garden this year, but it will be a major challenge working out the priorities and policies for the future, especially as the climate appears to be entering a very unpredictable phase affecting decisions about the range of plants to be used.
Still, the team seem to be a pretty content bunch, even though on occasions paperwork and ‘office stuff’ may get in the way of being outside and doing what they love. As Allison says, even the laborious turning of the compost heaps can sometimes be rewarding:
‘.. it gives you a good workout and you can find a surprising number of lost hand tools!’

Gardener in charge Allison Napier- normally not sitting on the compost, but turning it!
Acknowledgement: thanks to Allison, Jenny and Janet, the Peckover Gardening Team for their contributions.
Quizzicals:
- Hello Miss Black – Hyacinth
- A punch up in the water – hydrophyte
Old School Gardener
If you’ve enjoyed reading this post and others on this blog, why not comment and also join some other people and sign up for automatic updates via email (see side bar, above right ) or through an RSS feed (see top of page)?